-
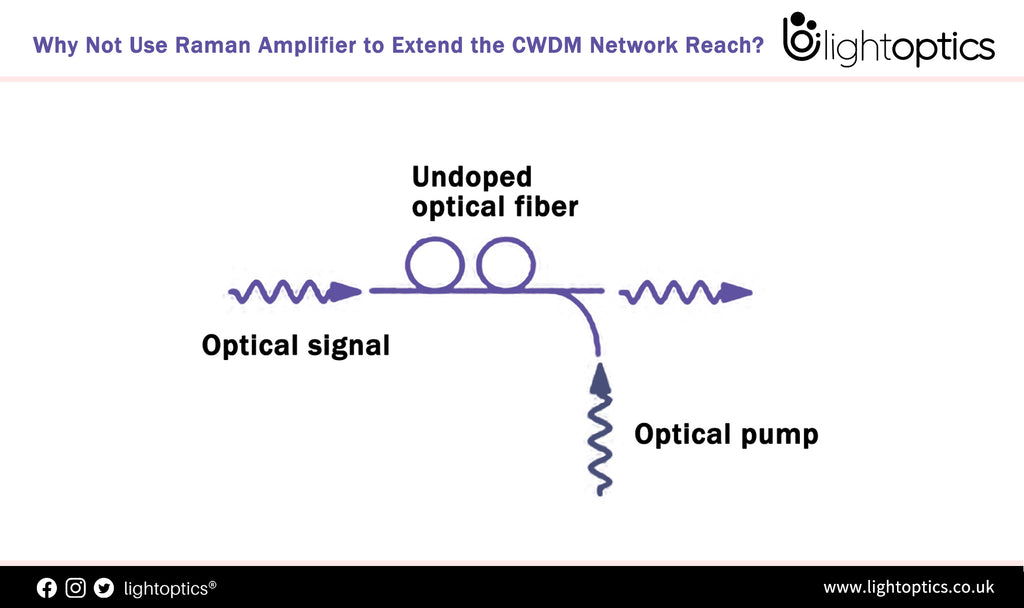
Why Not Use Raman Amplifier to Extend the CWDM Network Reach?
In comparison with the long-haul DWDM network that uses the thermo-electric coolers to stabilize the laser emissions essential, CWDM technology employs wider wavelength spacing and less expensive components, allowing the wavelength fluctuation of uncooled directly modulated laser diodes (DMLs). But on the other hand, the CWDM network exists the limitation for the uncooled DMLs’ output power and the additional loss of CWDM Mux Demux... -
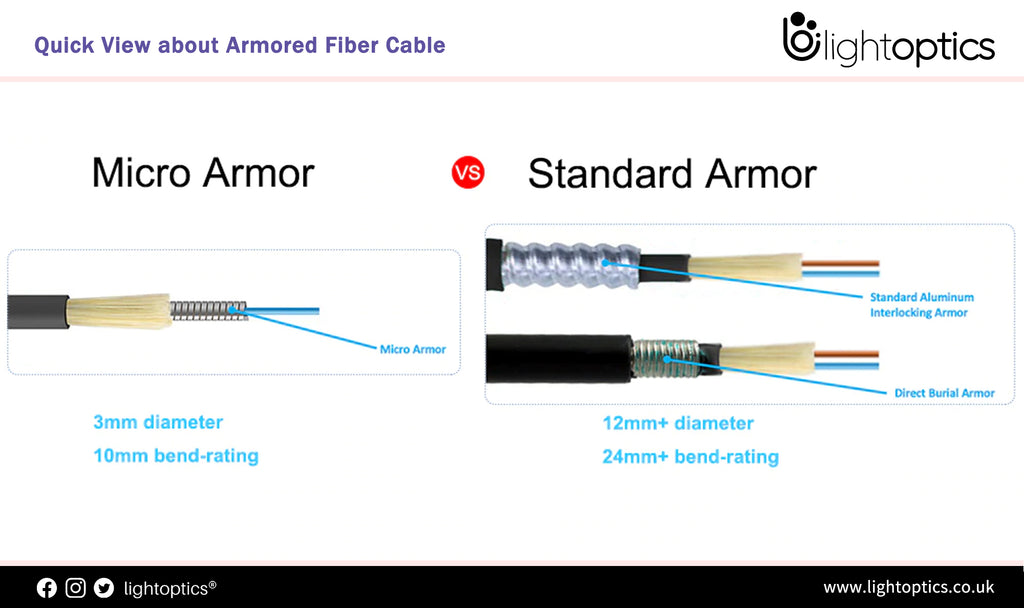
Quick View about Armored Fiber Cable
Tired of broken fiber optic patch cords? Micro Armor Fiber Cable is the ideal optical for you, never break a patch cord again! As is known, armored fiber cable can provide extra protection for fiber optic cable without sacrificing flexibility or functionality within fiber networks, featuring more robust and reliable when encountered with rodents, moisture, and other issues that may cause damage. The armored fiber cable is now optimal... -
Active Tap vs Passive Tap
When talking about network security and monitoring solutions, network access devices are the very first step in building an advanced visibility platform. The two most popular ways of monitoring traffic are using Network TAPs or port mirroring through a SPAN port. As covered in this article, a network TAP provides the most accurate way to copy the actual traffic that runs through a system... -
Fiber to the Desk (FTTD): Advantage, Deploy and Solution
In recent years, projects like FTTH (Fiber to the Home) and FTTB (Fiber to the Building) are carried out to provide better services for customers. To future capitalize on the benefits of optical cable, Fiber to the Desk (FTTD) is recommended for enterprises, financial institutions and federal agencies, which need high security and high data transmission speed. This article will guide you to have... -
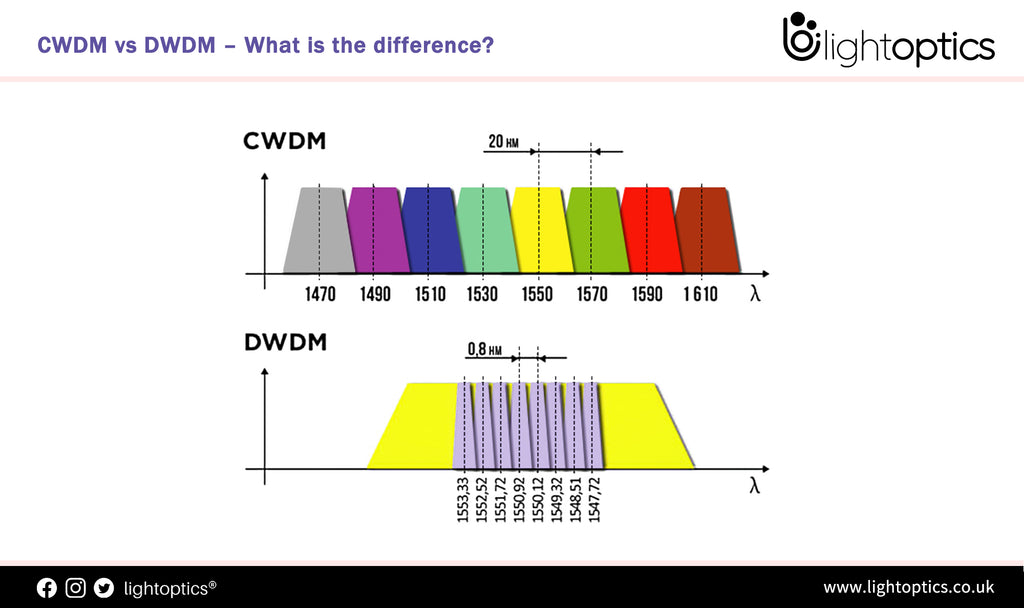
CWDM vs DWDM – What is the difference?
Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexers (CWDM) : CWDM stands for Coarse wavelength division multiplexers. A CWDM system commonly supports eight wavelengths per fiber and is designed for short-range communications, using wide-range frequencies with wavelengths spread far apart. These are modules that increases the amount of bandwidth the fiber optic system will carry by transmitting multiple signals at various wavelengths along the fiber optic cables. Since... -
FHD4 Series MTP/MPO Cassettes Module Solution
What Is Modular MTP/MPO Cassettes? MTP Cassette, as an easy-to-install and cost-effective plug-and-play cable management solution in today’s fiber optic cable patching system, is used to interconnect MTP backbones with LC or SC patching. Providing secure transition between MTP and LC or SC discrete connectors, they allow for rapid deployment of data center infrastructure as well as improved troubleshooting and reconfiguration during MACs (moves,... -
What is Fiber to the Home (FTTH)?
What is FTTH Meaning? Fiber to the home (FTTH) is a fiber optic communication delivery form where the fiber extends from a central office to the boundary of a home living space or business office. Once it reaches the home or business office, the signal is conveyed throughout the space using coaxial cable, wireless, optical fibers or power line communication. FTTH includes various flavors of... -
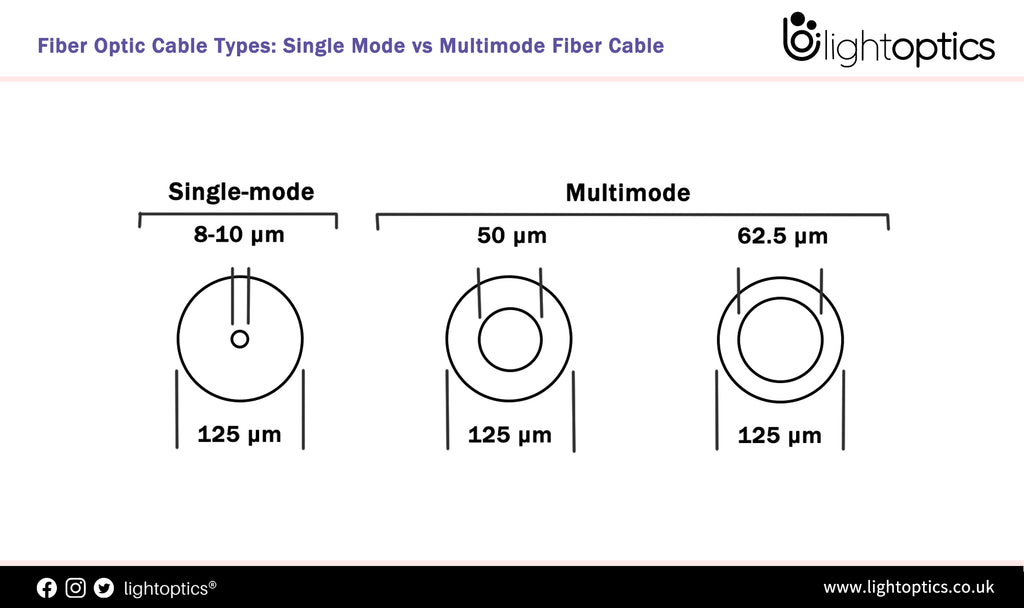
Fiber Optic Cable Types: Single Mode vs Multimode Fiber Cable
Single Mode and multimode Fiber Cable, both these types of optical fibers have their own attributes and are used as per the specific requirements. The differences between single mode and multimode fiber optic cable mainly lie in fiber core diameter, wavelength & light source, bandwidth, color sheath, distance and cost. An optical fiber consists of a core surrounded by cladding where the core is... -
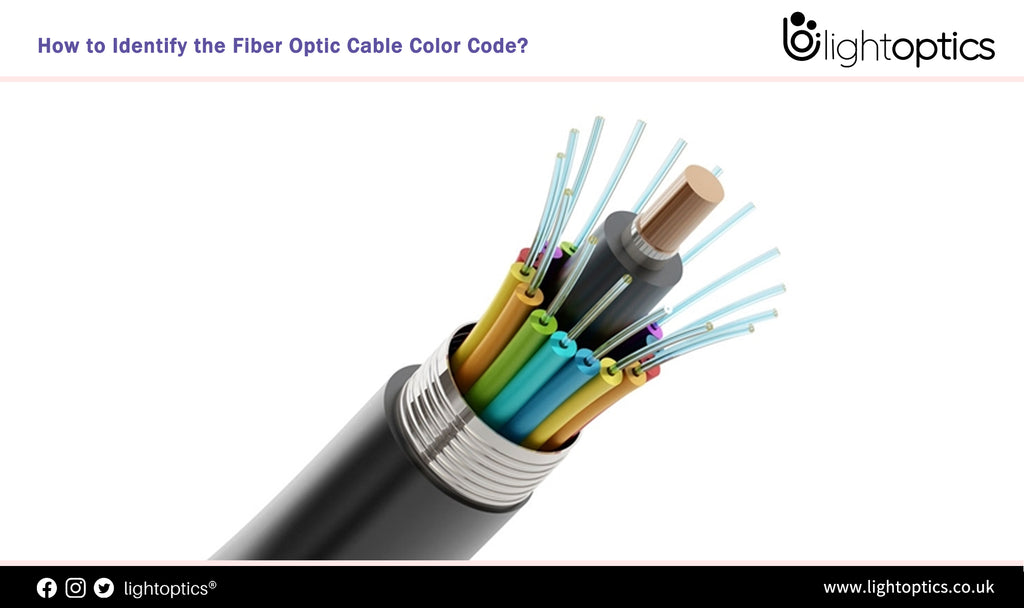
How to Identify the Fiber Optic Cable Color Code?
Fiber Optic Cable Outer Jacket Color Code Fiber cable jacket is made of various types of materials. Colored outer jackets or print may be used on outside plant and premises fiber cables, e.g., fiber distribution cables, fiber optic patch cords, etc. In EIA/TIA-598, the fiber color code defines the jacket color codes for different fiber types. It’s important to consider the jacket type when selecting... -
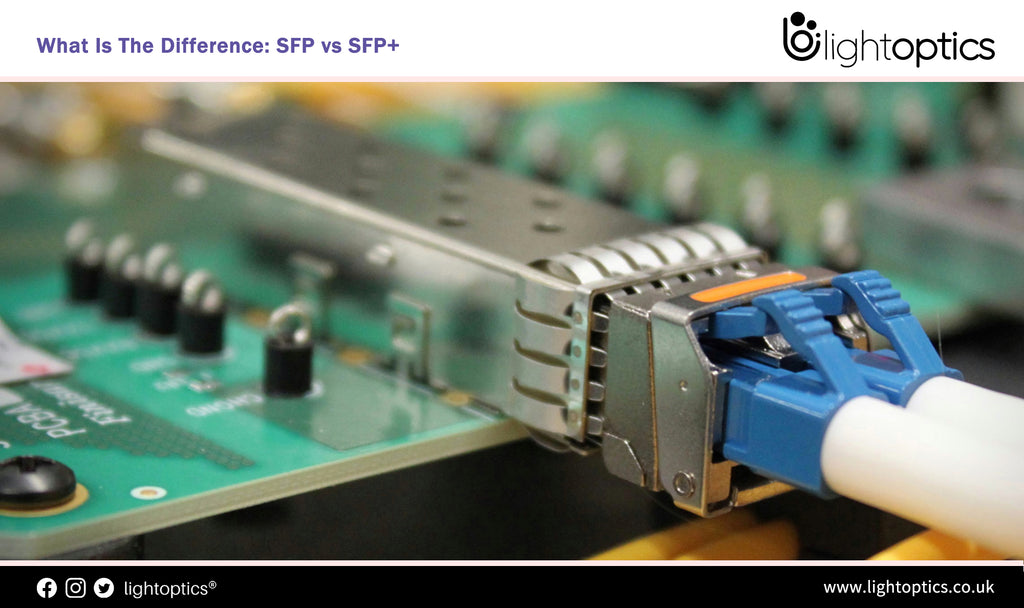
What Is The Difference: SFP vs SFP+
Today there are different optical transceivers available on the market. They come in various form factors offering speeds from 100Mbps to 100Gbps and are fully compliant to the MSA and IEEE 802.3 standards. Some of the more popular form factors include SFP, SFP+, XFP, GBIC, XENPAK, QSFP and QSFP28. As we know, a SFP module just looks the same as the SFP+ module. And most...
Customer Service: sales@lightoptics.co.uk
Shopping Cart
0
Close
Your Cart
Your cart is currently empty.