-
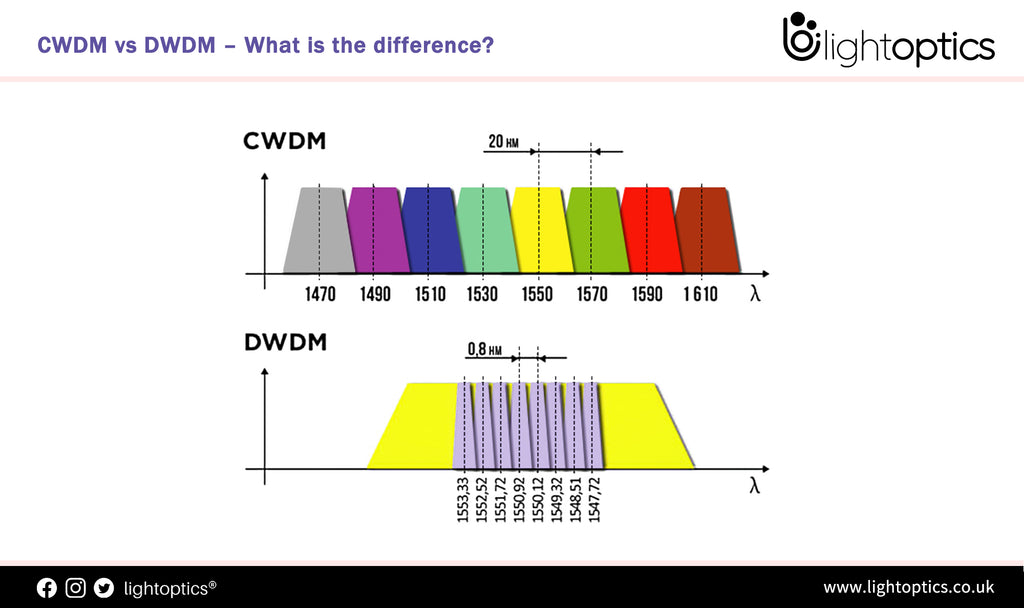
CWDM vs DWDM – What is the difference?
Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexers (CWDM) : CWDM stands for Coarse wavelength division multiplexers. A CWDM system commonly supports eight wavelengths per fiber and is designed for short-range communications, using wide-range frequencies with wavelengths spread far apart. These are modules that increases the amount of bandwidth the fiber optic system will carry by transmitting multiple signals at various wavelengths along the fiber optic cables. Since... -
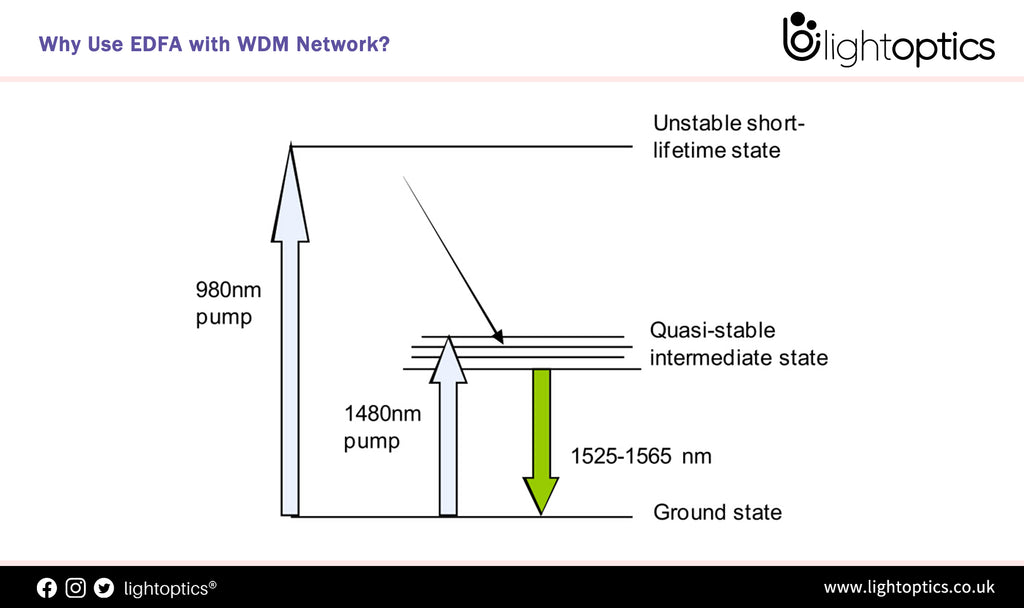
Why Use EDFA with WDM Network?
EDFA (erbium doped fiber amplifier), commercialized in the early 1990’s, became a key enabling technology for optical communication networks, and has deployed in the field. It is usually used to improve the intensity of optical signals being carried through a fiber optical communication system thus enables the optical signals in an optical fiber to be amplified directly in high bit rate systems beyond Terabits. As the... -
Different Ports on WDM Mux/Demux
WDM (wavelength-division multiplexing) is a commonly used technology in optical communications, which is one of the most common way of using wavelengths to increase bandwidth by multiplexing various optical carrier signals onto a single optical fiber. CWDM (coarse wavelength-division multiplexing) and DWDM(dense wavelength-division multiplexing) MUX/DEMUX(multiplexer/demultiplexer) are two important components in WDM systems, which are often deployed to join multiple wavelengths onto a single fiber. There are... -
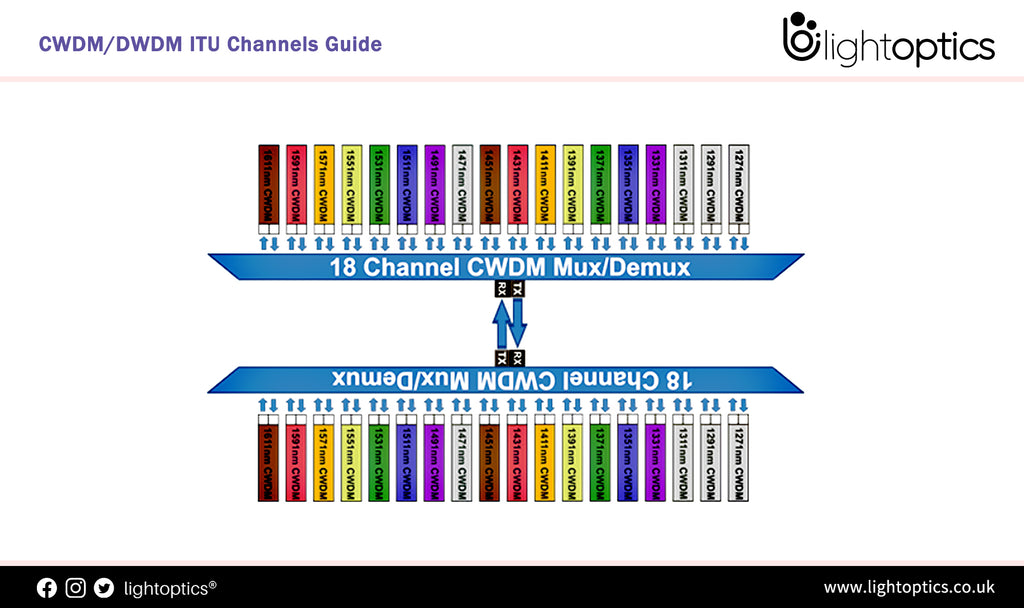
CWDM/DWDM ITU Channels Guide
Understand CWDM/DWDM ITU Channels
Customer Service: sales@lightoptics.co.uk
Shopping Cart
0
Close
Your Cart
Your cart is currently empty.